AI-generated imagery has burst onto the scene, offering a powerful way for anyone to create stunning visuals from simple text prompts.
This technology is a game-changer for digital art and content creation. However, anyone who has used these tools knows it's not always a smooth ride.
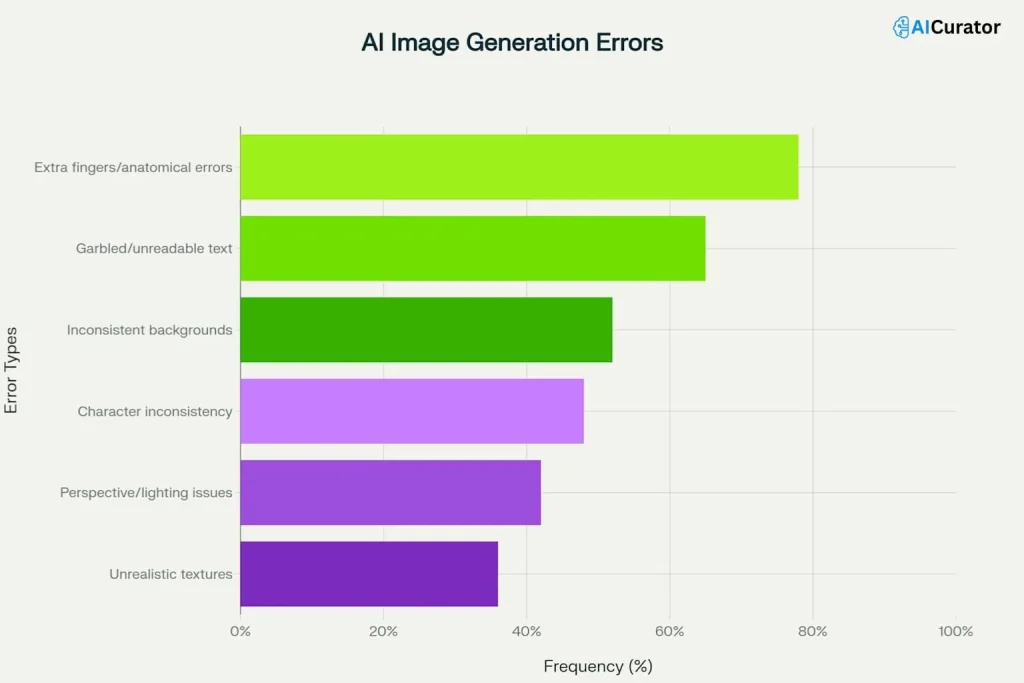
Often, the results are plagued by strange errors, from mangled text to six-fingered hands, turning creative dreams into frustrating fails.
Understanding why these glitches happen and learning how to fix them is the key to access the true potential of AI as a creative tool and avoid the most common AI Image Fail pitfalls
The Root of the Problem: Why AI Image Generators Make Mistakes
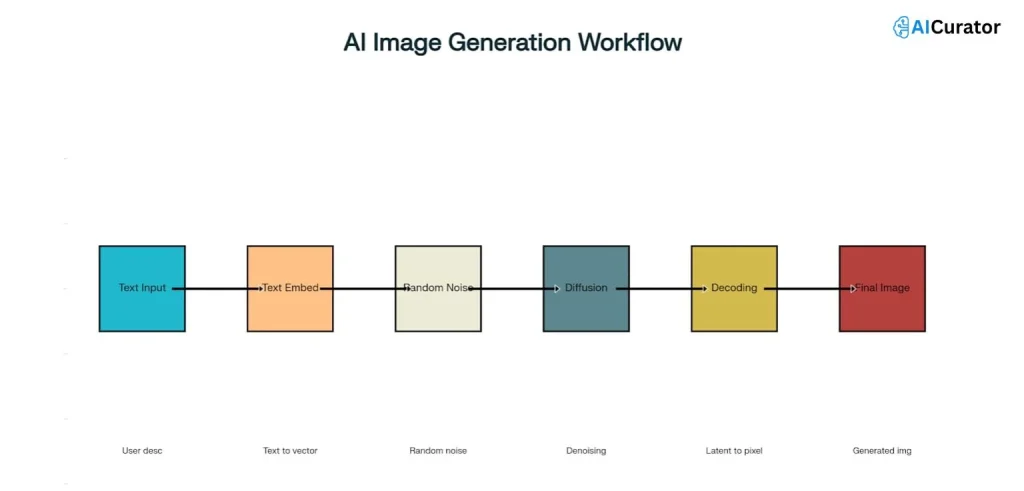
AI image models don't “understand” the world like humans do; they recognise patterns from vast datasets of images and text. This pattern-matching approach, while powerful, is also the source of many common errors.
1. The Art and Science of Prompt Engineering
The words you use to guide the AI are the most vital part of the process. Yet, crafting the perfect prompt is a major hurdle. A slight change in wording can produce wildly different images, and a prompt that works wonders in one model might fail in another.
This lack of a standard language for prompts means users often rely on trial and error to get what they want. Vague or contradictory prompts confuse the AI, leading to disjointed or messy results.
2. Anatomical Oddities and Uncanny Valleys

AI models frequently struggle with getting human and animal anatomy right.
You've likely seen images with extra fingers, twisted limbs, or strange facial proportions. This happens because the AI doesn’t have a structured, biological knowledge of anatomy.
It generates a hand by blending statistical averages of hands from its training data, not by constructing a hand with five distinct fingers.
Deviations from common poses can easily lead to these distortions.
3. The Gibberish Text Phenomenon
One of the most common AI art fails is its inability to render legible text. Words can appear as a jumble of nonsensical characters, misspelled, or awkwardly placed within the image. The reason is simple: most AI image models are trained on visual data, not language. They learn what text looks like as a shape or pattern, but not what it actually says.
The AI treats a word as just another visual element to be drawn, like a tree or a cloud, without understanding its meaning.
4. Incoherent Backgrounds and Wonky Physics
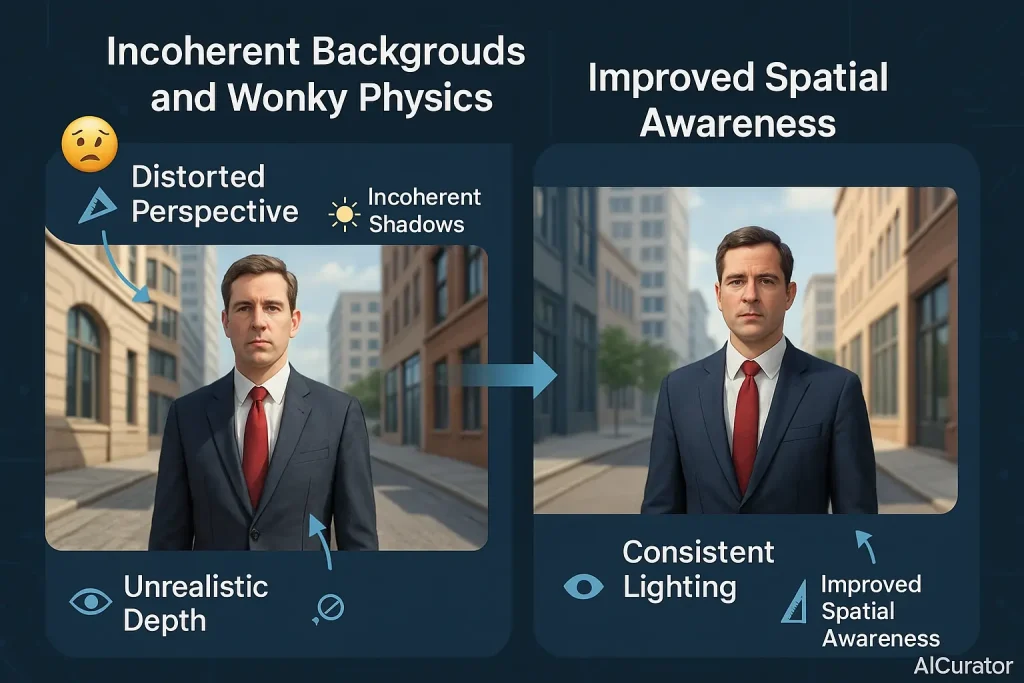
AI-generated backgrounds can often feel “off,” with strange perspectives, or lighting and shadows that don't match the main subject. This occurs because diffusion models tend to see the background as less important than the foreground subject.
This leads to problems with depth, how objects relate to each other, and the overall context of the environment, making the final image feel unrealistic.
5. The Challenge of Character Consistency
Creating a series of images featuring the same character is a significant challenge. Because the AI treats every image generation as a new and independent task, maintaining a consistent face, hairstyle, or outfit across multiple pictures is difficult.
Even using the exact same prompt can result in subtle (or not-so-subtle) changes between images, which is a major problem for storytelling or branding projects.
6. A Lack of Precise Control
Despite how impressive the outputs can be, a fundamental issue with AI image generation is the user's lack of fine-tuned control. You might struggle to guide the model towards a specific artistic style or tweak small details.
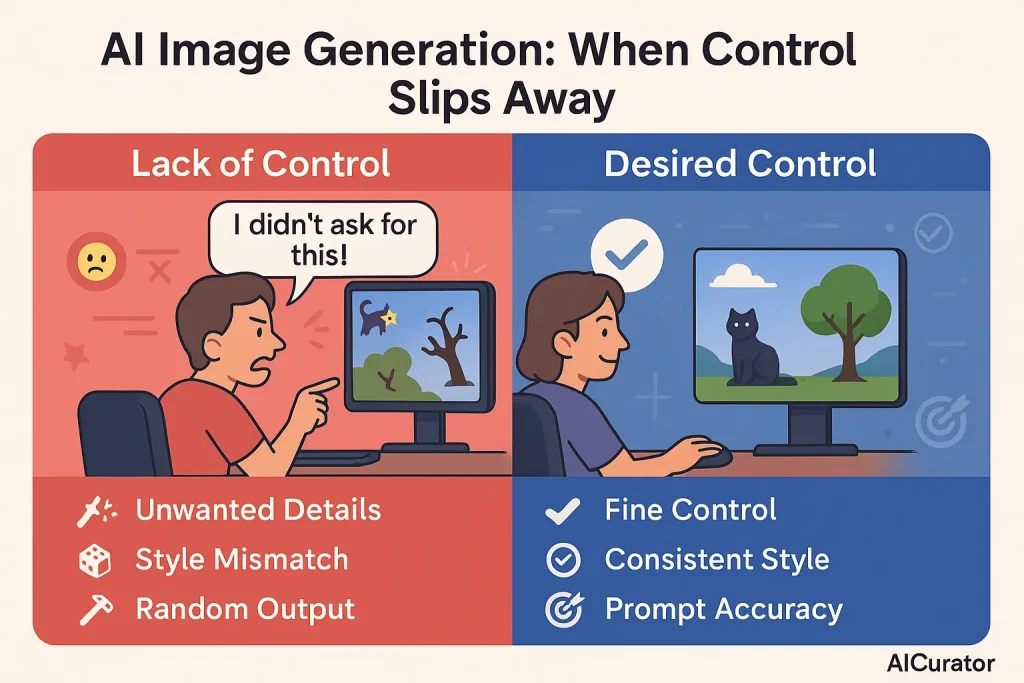
The AI works on probability, which can sometimes lead to surprising and unwanted elements appearing in your scene. The model might even misinterpret your instructions, adding strange details based on learned associations, making the process feel unpredictable.
A Practical Guide to Fixing AI Image Errors
Now for the good news: almost all of these errors can be managed or fixed. With the right techniques and tools, you can steer the AI toward your vision.
1. Mastering Your Prompts
Since the prompt is your primary tool, improving your prompting skills is the first step.
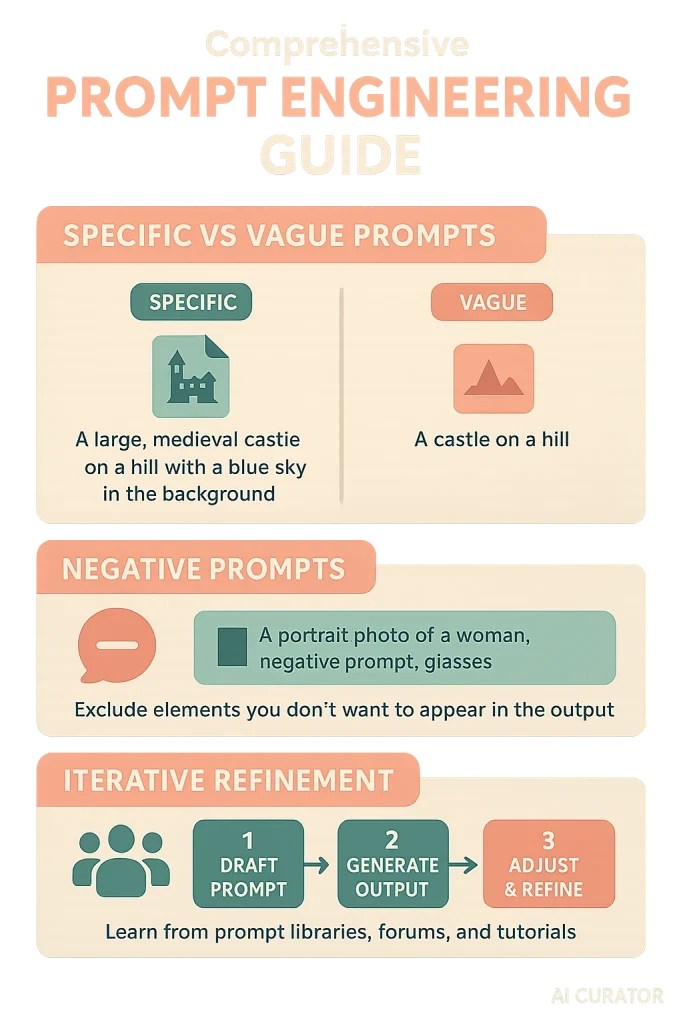
2. Correcting Anatomical Flaws
When the AI gets bodies wrong, you have several options for correction.
3. Solving Text-in-Image Troubles
Getting text right often requires a two-step process.
4. Building Believable Backgrounds
To fix incoherent backgrounds, you need to give the AI better environmental cues.
5. Achieving Character Consistency
Keeping your character looking the same requires giving the AI a strong reference point.

More from AICurator
Conclusion: Partnering with the AI
AI image generation is an incredibly powerful technology, but it's not a magic button. The errors and glitches it produces are a direct result of how these systems learn and process information.
By understanding these limitations—from its struggles with text and anatomy to its need for precise prompting—you can move from being a passive user to an active creator.
The key is to see the AI not as an infallible artist, but as a creative partner.
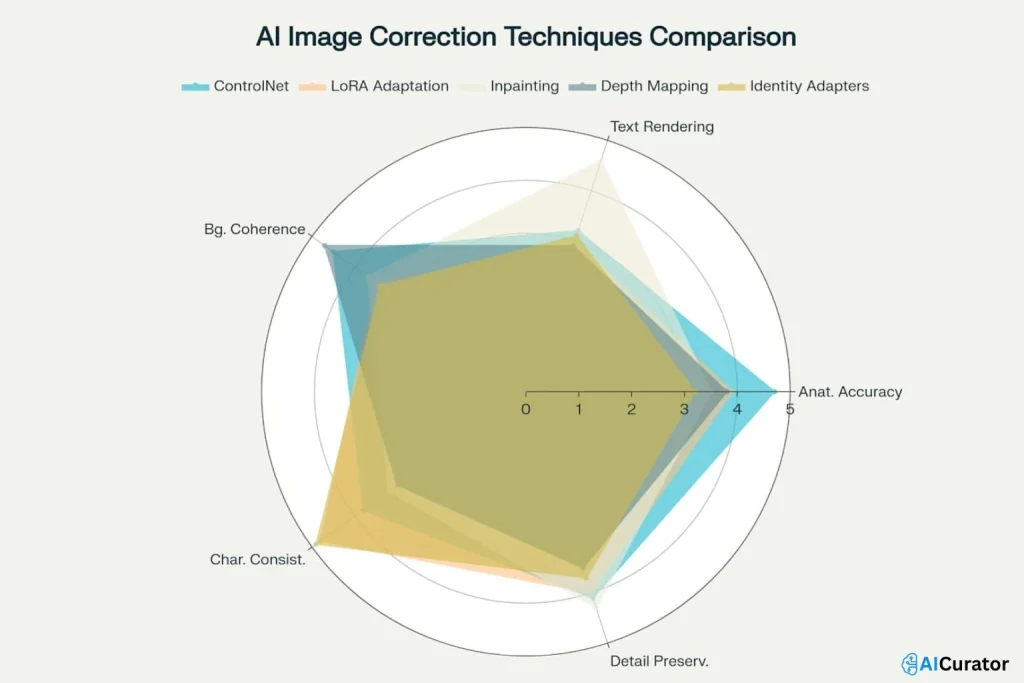
By combining smart prompt engineering, using advanced tools like ControlNets and LoRAs, and being willing to do a bit of post-processing, you can overcome its flaws and consistently produce high-quality, usable images that match your creative vision.
















